Introduction
In the intricate landscape of commerce and digital transactions, chargebacks play a crucial role in protecting consumers and maintaining the integrity of payment systems. These financial reversals are a mechanism designed to safeguard individuals from unauthorized or fraudulent transactions, billing errors, and unsatisfactory purchases. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of chargebacks, explore their implications for businesses and consumers, and offer actionable strategies to prevent and manage them effectively.
What are Chargebacks?
A chargeback, also known as a payment dispute or reversal, occurs when a consumer disputes a transaction on their credit card statement and requests a refund directly from their issuing bank or credit card company. This process bypasses the merchant, allowing consumers to seek resolution and regain their funds without direct involvement from the seller. Chargebacks serve as a safety net for consumers, providing recourse against fraudulent activities, billing mistakes, and unauthorized purchases.
Understanding the Chargeback Process
The chargeback process typically involves the following stages:
Customer Dispute: The consumer identifies a transaction they believe is erroneous, unauthorized, or fraudulent and initiates a chargeback with their bank.
Issuing Bank Review: The issuing bank assesses the validity of the dispute and gathers relevant information, including transaction details and supporting documentation from the cardholder.
Merchant Response: The merchant is notified of the chargeback and has an opportunity to respond with evidence demonstrating the transaction's legitimacy, such as order details, shipment tracking, or customer communication.
Bank Adjudication: The issuing bank reviews the evidence from both sides and makes a decision on whether the chargeback is valid. If the chargeback is upheld, the funds are returned to the cardholder; if not, the merchant retains the funds.
Implications for Merchants
Chargebacks can have significant implications for merchants, including:
Financial Loss: Chargebacks result in the reversal of funds, leading to immediate financial losses for the merchant. Additionally, merchants may incur chargeback fees from payment processors.
Reputational Damage: High chargeback rates can damage a merchant's reputation, as they may be perceived as unreliable or engaging in fraudulent activities.
Administrative Burden: Addressing chargebacks requires time and resources, diverting attention from core business operations.
Increased Costs: Merchants with high chargeback rates may face higher processing fees and penalties from payment processors or card networks.
Preventing and Managing Chargebacks
While chargebacks are a natural part of the payment ecosystem, merchants can take proactive steps to minimize their occurrence:
Transparent Policies: Clearly communicate refund, return, and cancellation policies to manage customer expectations and reduce disputes.
Accurate Descriptions: Provide accurate and comprehensive product or service descriptions, reducing the likelihood of customer dissatisfaction.
Robust Customer Support: Offer responsive and helpful customer service to address concerns promptly and effectively.
Secure Payment Processing: Implement stringent security measures to safeguard customer data and prevent unauthorized transactions.
Fraud Detection Tools: Utilize advanced fraud detection systems to identify and prevent potential fraudulent transactions.
Effective Communication: Keep customers informed about order confirmations, shipping details, and potential delays to avoid misunderstandings.
Documentation: Maintain thorough records of transactions, communication, and customer interactions to provide evidence in case of disputes.
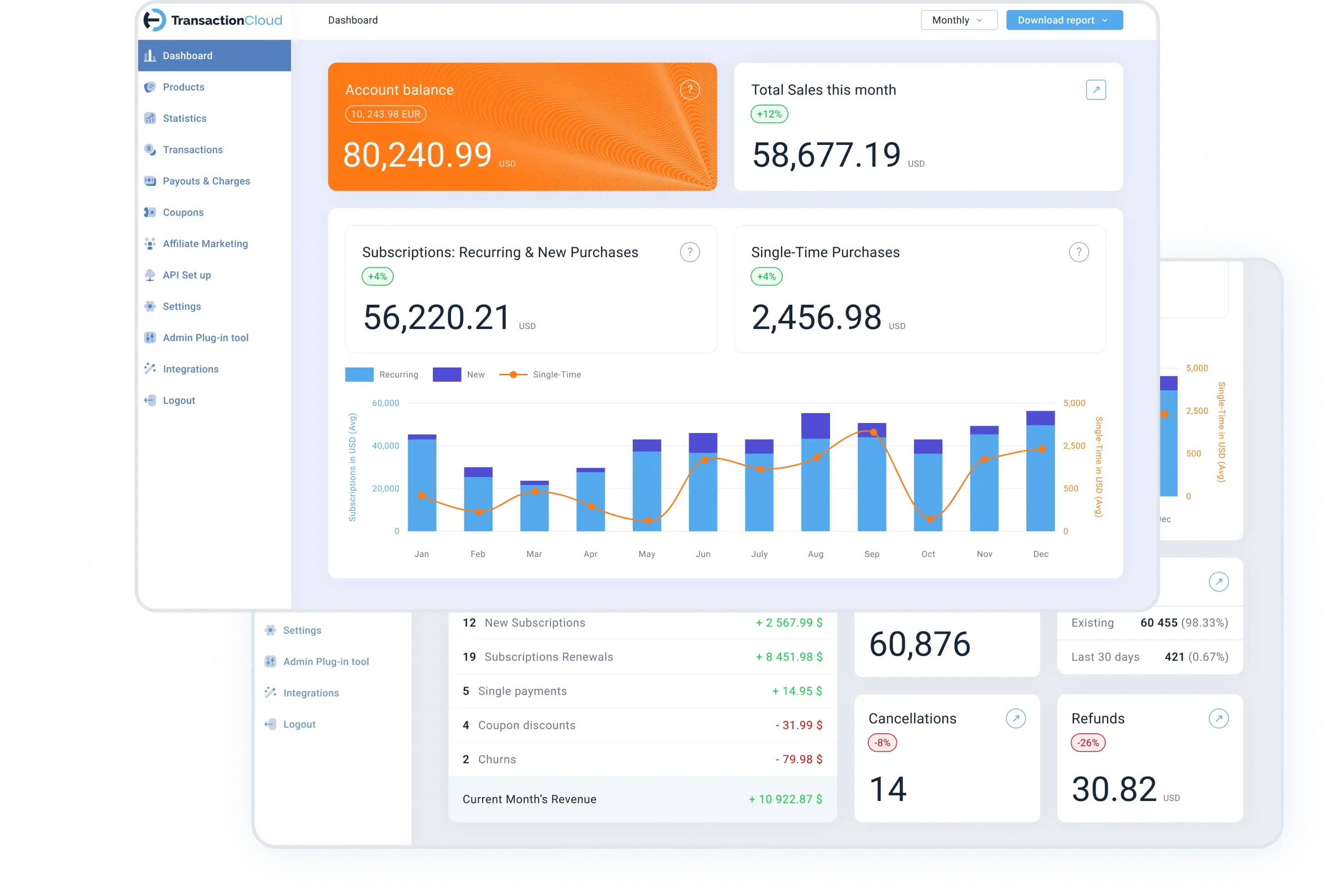
With Transaction Cloud you can track your chargebacks with notifications to minimize their occurrence.
Conclusion
Chargebacks serve as a critical consumer protection tool in the digital payment landscape, enabling individuals to dispute unauthorized or fraudulent transactions. While they are intended to safeguard consumers, chargebacks can pose challenges for merchants, leading to financial losses and reputational damage. By adopting a proactive approach that emphasizes transparent policies, strong customer service, robust security measures, and effective communication, merchants can minimize chargebacks and create a more secure and trustworthy transaction environment. Striking the right balance between consumer protection and merchant stability is key to ensuring a smooth and reliable payment experience for all parties involved.